What Is an HVAC Zoning System and Is It Right for Your Home?
Are you tired of arguing with family members over the temperature in your home? Do you have rooms that are always too hot or too cold? An HVAC zoning system might be the solution you’re looking for.
By dividing your home into multiple zones, each controlled by its own thermostat, you can set the ideal temperature for each room. This not only improves comfort but can also lead to energy savings.
A zoned HVAC system gives you more control over your indoor climate, potentially extending the lifespan of your equipment. But is it right for your home? Let’s explore the benefits and potential drawbacks.
Key Takeaways
- HVAC zoning systems allow for multiple temperature zones in a single home.
- This can lead to improved comfort and energy efficiency.
- Zoned systems can help eliminate temperature discrepancies between rooms.
- They may extend the lifespan of your HVAC equipment.
- Homeowners with specific temperature control issues may benefit most.
Understanding HVAC Zoning Systems
HVAC zoning systems are designed to provide customized comfort by dividing a home into distinct temperature-controlled areas or “zones.” This approach allows homeowners to tailor the temperature in different parts of their home according to specific needs and preferences.
Definition and Basic Concept
An HVAC zoning system is a sophisticated climate control solution that recognizes the varying heating and cooling needs of different areas within a home. By dividing the home into multiple zones, typically based on usage patterns, occupancy, and comfort preferences, these systems can offer more precise temperature control.
Each zone is equipped with its own thermostat and dampers within the ductwork to control airflow, allowing for a more tailored approach to heating and cooling. The basic concept behind zoning is that different areas of a home have different temperature requirements due to factors such as sun exposure, room usage, and personal preferences.
- Divides the home into distinct temperature-controlled areas or “zones”
- Recognizes varying heating and cooling needs based on factors like sun exposure and room usage
- Equips each zone with its own thermostat and dampers for controlled airflow
How HVAC Zoning Differs from Traditional Systems
Traditional HVAC systems rely on a single thermostat to control the temperature throughout the entire home, often resulting in uneven heating or cooling and energy waste. In contrast, HVAC zoning systems allow for customized temperature settings in different areas, addressing the limitations of traditional systems.
By treating the home as a collection of micro-environments rather than a single space, zoning systems provide a more sophisticated approach to climate control. This results in enhanced comfort and potentially significant energy savings.
How HVAC Zoning Systems Work

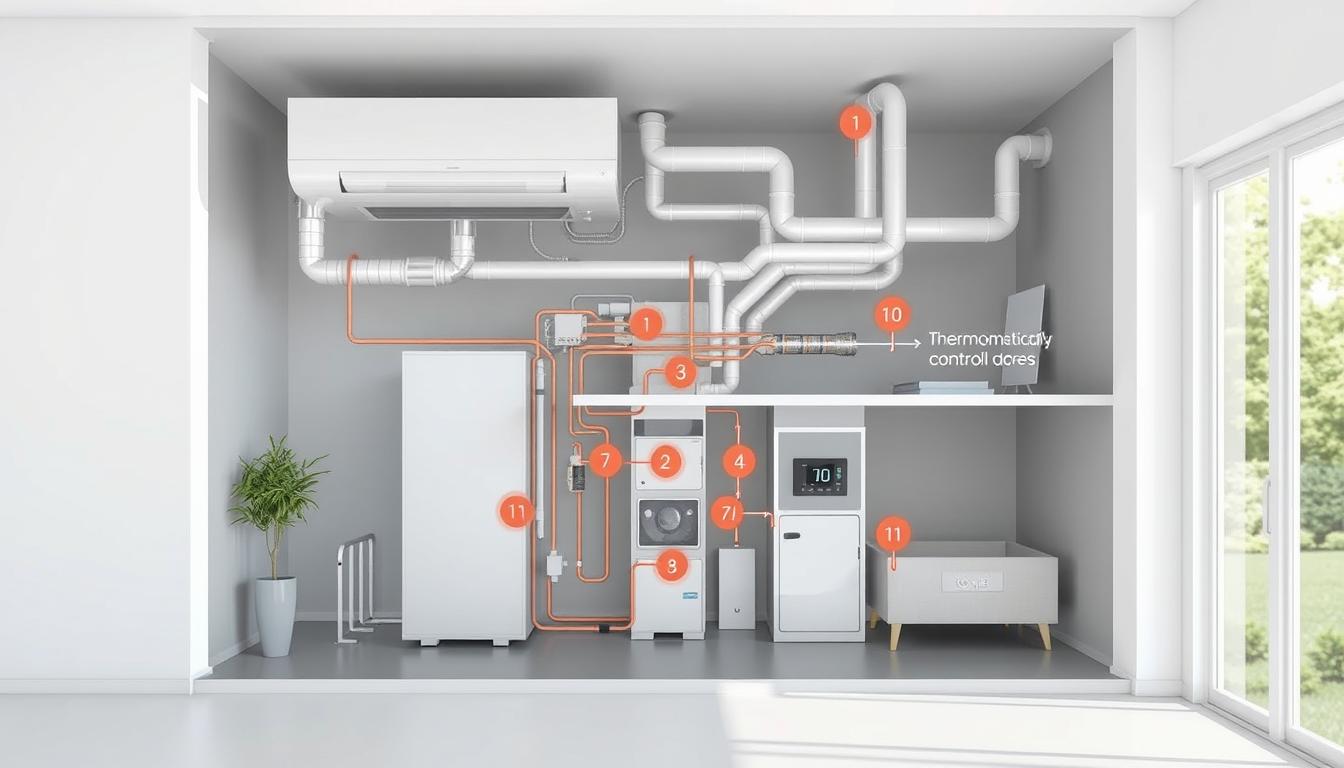
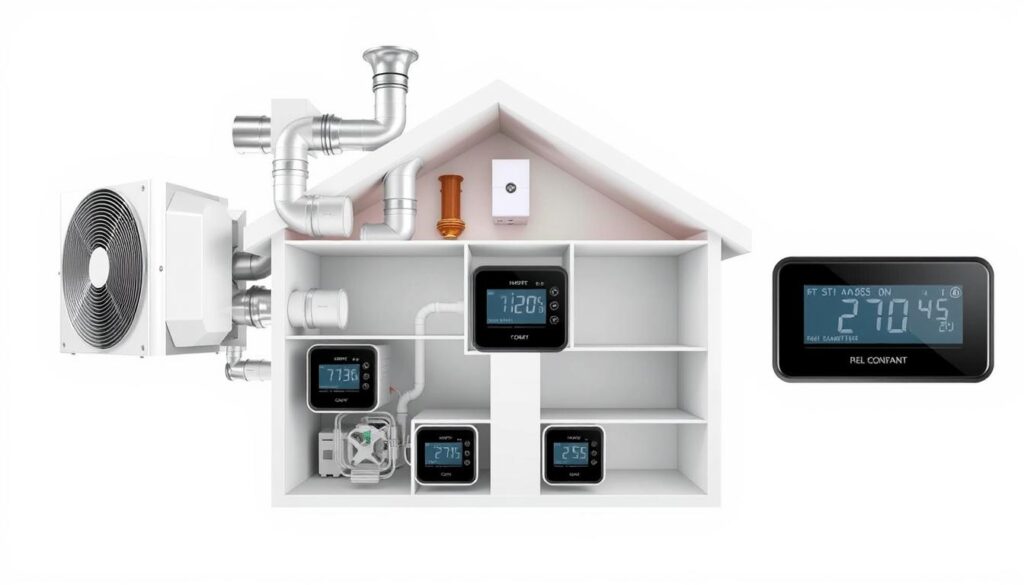
To appreciate the benefits of HVAC zoning, it’s essential to grasp how these systems function and regulate airflow. AnHVAC zoning systemoperates through a network of thermostats, dampers, and a central control panel, working together to provide precise temperature control in different areas of your home.
Key Components of a Zoned System
A zoned HVAC system consists of three primary components: multiple thermostats, automated dampers, and a central control panel. The first step in setting up a residentialHVAC zoning systemis to divide your home into zones. Once your home is divided into two or more zones, athermostatwill be installed within each zone. These thermostats are connected to onecentral control panelin your home.
The Role of Dampers and Thermostats
Thedampersin an HVAC zoning system function as “traffic controllers” for your conditioned air, opening and closing within your ductwork to direct airflow precisely where it’s needed. Each zone’s dedicatedthermostatmonitors the temperature and communicates with thecentral control panelwhen heating or cooling is required. When a specific zone’s thermostat detects a deviation from the set temperature, it sends a signal to the control panel.
Central Control Panel Functionality
Thecentral control panelserves as the “brain” of theHVAC system, receiving information from all thermostats and coordinatingdamperoperations to maintain desired temperatures in each zone. It signals the correspondingdampersin the ductwork toopen or close, regulating airflow to that zone. This targeted approach ensures that conditionedairis directed only where needed, increasing energy efficiency and comfort.
By understanding how these components work together, homeowners can appreciate the complexity and benefits of anHVAC zoning system. The system’s ability to control temperature in different zones enhances overall comfort and can lead to significant energy savings.
Types of HVAC Zoning Solutions
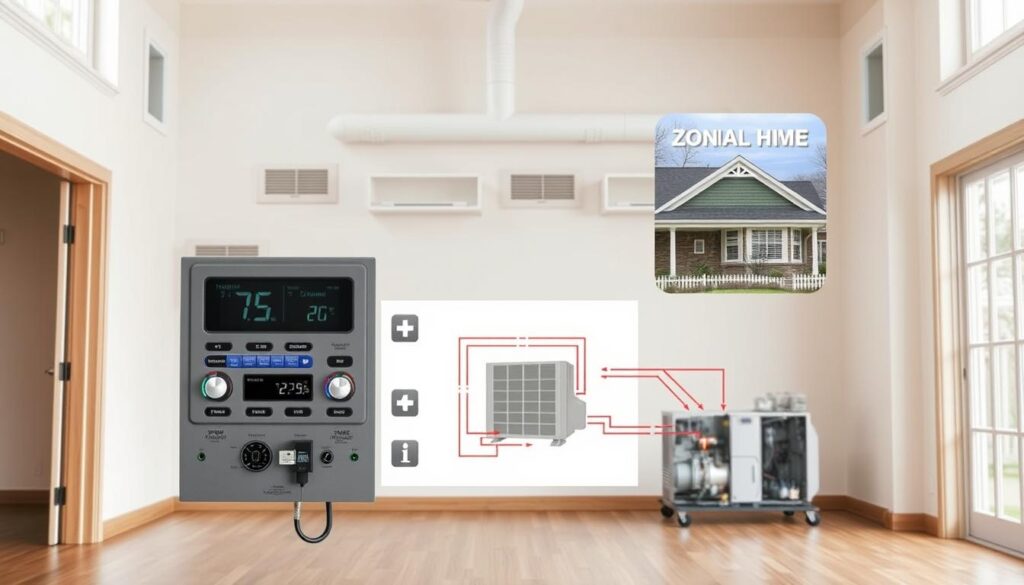
When considering an HVAC zoning system, it’s essential to understand the different types available. Homeowners can choose from various solutions, each designed to cater to specific needs and preferences. The primary types of HVAC zoning solutions include manual damper systems, automatic damper systems, and ductless mini-split zoning options.
Manual Damper Systems
Manual damper systems are the most basic and affordable zoning option. These systems involve installing dampers in the ductwork, which are adjusted manually to redirect airflow between zones. For instance, in the summer, cold air tends to sink, so you might need to adjust the dampers to push more cool air upstairs. Conversely, in the winter, you’ll want to adjust the dampers to direct more hot air downstairs since heat rises. This process requires seasonal adjustments to maintain optimal comfort and efficiency.
Automatic Damper Systems
Automatic damper systems are the most common zoning solution and offer greater convenience than manual systems. These systems feature motorized dampers that automatically adjust based on readings from multiple thermostats. The motors can open and close the dampers to varying degrees, depending on the specific heating or cooling needs of each zone. This level of control allows for more precise temperature management and can significantly enhance the overall comfort and efficiency of the HVAC system.
Ductless Mini-Split Zoning Options
Ductless mini-split systems offer an alternative approach to zoning that doesn’t require existing ductwork. These systems can condition the air in individual spaces or zones, providing a high degree of customization. Typically, a mini-split system conditions the air in one room, but you have the option of installing multiple heads to a single unit, allowing for greater flexibility. This makes ductless mini-splits an ideal solution for home additions or retrofits where installing new ductwork might be impractical.
In conclusion, the choice of HVAC zoning solution depends on various factors, including budget, existing infrastructure, and desired level of automation. By understanding the different types of zoning systems available, homeowners can make an informed decision that best suits their needs.
Benefits of Installing HVAC Zoning Systems
HVAC zoning systems offer numerous benefits for homeowners seeking improved comfort and energy savings. By allowing for more precise temperature control, these systems can significantly enhance the living experience in homes of various sizes and configurations.
Enhanced Comfort and Temperature Control
One of the primary advantages of an HVAC zoning system is its ability to provide enhanced comfort through personalized temperature control. With multiple thermostats, homeowners can set ideal temperatures for different areas or zones within their home, eliminating hot and cold spots. This means that each room can be conditioned according to its specific needs and the preferences of its occupants.
For instance, bedrooms can be kept cooler at night, while living areas remain at a comfortable temperature. This level of control not only improves overall comfort but also allows for a more tailored heating and cooling experience.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
HVAC zoning systems are also renowned for their energy efficiency and potential for cost savings. By only conditioning the spaces that need it, rather than the entire home, these systems can significantly reduce energy consumption. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, HVAC zoning can lead to a 30% reduction in energy costs.
| Energy Savings Potential | Traditional HVAC | Zoned HVAC System |
|---|---|---|
| Annual Energy Consumption | 100% | 70% |
| Energy Costs | $1,000 | $700 |
As highlighted by the U.S. Department of Energy’s estimate, the potential for energy savings with HVAC zoning is substantial. By reducing the workload on the HVAC equipment, homeowners can enjoy lower utility bills and a more environmentally friendly heating and cooling solution.
“By implementing HVAC zoning, homeowners can achieve significant reductions in their energy bills while maintaining a comfortable living environment.”
Extended Equipment Lifespan
In addition to comfort and energy efficiency benefits, HVAC zoning systems can also contribute to an extended equipment lifespan. By reducing the runtime and cycling of HVAC equipment, zoning decreases the wear and tear on the system. This can potentially prolong the system’s lifespan and reduce the need for frequent repairs or replacements.
With a zoned HVAC system, the equipment operates more efficiently, as it is not required to work as hard to maintain a uniform temperature throughout the home. This reduced strain can lead to cost savings over time, as homeowners may avoid premature replacement costs.
Ideal Home Situations for HVAC Zoning
Certain home situations greatly benefit from the installation of HVAC zoning systems, enhancing comfort and efficiency. HVAC zoning is not a one-size-fits-all solution, but it is particularly advantageous for homes that experience temperature variations or have specific heating and cooling needs.
Multi-Level Homes and Temperature Variations
Multi-level homes often suffer from temperature stratification, where heat rises to the upper levels, leaving the lower levels cooler. A zoned HVAC system allows homeowners to control the temperature on each level independently, ensuring a more uniform and comfortable temperature throughout the home. This is particularly beneficial in homes where the upstairs areas feel significantly warmer than the downstairs areas.
Homes with High Ceilings or Large Windows
Homes with high ceilings or large windows present unique temperature control challenges. High ceilings can lead to heat accumulation at the top, making the lower areas feel cooler. Similarly, large windows can let in significant amounts of sunlight, heating up a room. Zoned HVAC systems can address these issues by allowing for targeted heating and cooling, ensuring that rooms with these features are maintained at a comfortable temperature without affecting the rest of the house.
Rooms with Special Temperature Requirements
Some rooms in a home have special temperature requirements. For example, home offices with heat-generating equipment may require cooler temperatures, while nurseries or living areas may need consistent, warmer temperatures. HVAC zoning enables homeowners to create separate zones for these rooms, ensuring they are heated or cooled according to their specific needs without wasting energy on other areas of the home.
Solving Hot and Cold Spot Problems
Persistent hot and cold spots are a common issue in many homes, often resulting from inadequate HVAC system design or installation. Zoned HVAC systems can effectively resolve these issues by directing heated or cooled air precisely where it’s needed. This not only enhances comfort but also reduces the strain on the HVAC system, potentially extending its lifespan.
| Home Situation | Benefit of HVAC Zoning |
|---|---|
| Multi-Level Homes | Controls temperature on each level independently |
| Homes with High Ceilings or Large Windows | Targets heating and cooling to specific areas |
| Rooms with Special Temperature Requirements | Creates separate zones for specific temperature needs |
| Homes with Hot and Cold Spots | Directs heated or cooled air to specific areas |
Cost Considerations for HVAC Zoning
Understanding the costs associated with HVAC zoning is crucial for homeowners considering this upgrade. The total cost of an HVAC zoning system includes several factors, from initial installation expenses to long-term energy savings and maintenance costs.
Initial Installation Expenses
The initial cost of zoning equipment and installation for a zoned HVAC system can range between $1,700 and $4,500, according to HomeGuide. However, this estimate does not include costs associated with replacing existing HVAC components. The final cost also depends on the number of zones you’re looking to install.
If you’re overhauling an existing HVAC system with a zoned one, the cost will increase due to the need to remove the old system or upgrade it with dampers and new electric wiring. Installing a zoned HVAC system during new construction is typically more cost-effective.
| Installation Scenario | Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Existing ductwork with no zoning | $4,500 – $7,000 |
| No ductwork for zoning | $5,000 – $8,500 |
| New construction with zoning | $1,700 – $4,500 |
Potential Long-Term Energy Savings
While the initial installation cost of an HVAC zoning system can be significant, the potential long-term energy savings can help offset this expense. The U.S. Department of Energy estimates that zoning can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 30%.
Maintenance and Repair Costs
Maintenance is a crucial aspect to consider when evaluating the total cost of an HVAC zoning system. While zoned systems have more components that could potentially require service, proper maintenance can minimize these expenses. Regular checks and timely repairs can ensure the system operates efficiently and effectively.
Installation Process and Requirements
When it comes to HVAC zoning systems, the installation process differs greatly depending on whether you’re building from scratch or retrofitting an existing home. The complexity and cost of installation can vary significantly based on this factor.
New Construction vs. Retrofitting Existing Systems
In new constructions, HVAC zoning can be integrated into the design from the outset, making the installation process more straightforward and cost-effective. Homes built with zoning in mind typically have dedicated trunks and ducts for different areas, such as upstairs and downstairs, or specific rooms like the master bedroom. This pre-planning simplifies the installation of dampers, thermostats, and the zone panel. In contrast, retrofitting an existing home with an HVAC zoning system can be more complicated and expensive. It may require isolating runouts, placing dampers, or even replacing the existing ductwork with dedicated trunk lines.
Professional Installation Considerations
The installation of a zoned HVAC system requires professional expertise to ensure that it is done correctly and functions as intended. Proper system sizing and design are critical to achieve balanced airflow and optimal system performance. Qualified HVAC technicians understand the complexities of zoned systems and can properly configure all components, including dampers, thermostats, and control panels. While the installation process can take anywhere from 1 to 3 days depending on the complexity of the home and the existing heating and cooling system, the long-term benefits of enhanced comfort, energy efficiency, and potentially extended equipment lifespan make the investment worthwhile.
Potential Drawbacks of Zoned HVAC Systems
While zoned HVAC systems offer numerous benefits, they also come with some significant drawbacks that homeowners should consider. As with any major home improvement project, it’s essential to weigh the advantages against the potential disadvantages to make an informed decision.
Upfront Investment Concerns
One of the primary drawbacks of zoned HVAC systems is the significant upfront investment required. Converting a traditional central HVAC system to a zoned one can be expensive, potentially costing thousands of dollars. This expense can be a barrier for homeowners on a limited budget or those planning to sell their homes in the near future.
Installation Complexity and Disruption
The installation process for a zoned HVAC system can be complex and disruptive to daily life. Technicians may need to work in your home for several days, potentially opening walls and ceilings to access and modify existing ductwork. This process may require engaging multiple contractors, including electricians and drywall specialists, adding to the overall cost and inconvenience.
When Zoning May Not Be Worth It
Zoned HVAC systems are not suitable for every home. If you have a smaller house with consistent temperature patterns and no especially hot or cold spots, installing a zoned system may not be worth the hassle and expense. Homeowners should carefully assess their specific needs and consider alternative solutions, such as ceiling fans or improved insulation, before deciding on a zoned HVAC system.
Making the Right Decision for Your Home
When it comes to achieving optimal comfort in your home, anHVAC zoning systemis an option that deserves careful consideration. If you’re evaluating whether this system is right for you, it’s essential to weigh its benefits against the potential drawbacks.
AnHVAC zoning systemcan provide numerous advantages, including enhanced comfort and energy efficiency. However, it’s not suitable for every home. The higher installation cost, due to the need for multiple thermostats and dampers, can be a significant factor. Additionally, the increased complexity of the system may lead to higher repair costs over time.
To make an informed decision, consider the following key factors:
- Your home’s size and layout
- Existing comfort issues, such as temperature variations
- Budget constraints and potential long-term energy savings
- Your energy efficiency goals
It’s also crucial to consult with multipleHVAC professionalsto get assessments and quotes. Ensure that the contractors you work with have experience in installing zoning systems. When discussing your options with contractors, ask questions about the system’s design, installation process, and potential maintenance requirements.
If budget constraints are a concern, consider prioritizing the most problematic areas of your home and expanding the system later. By taking a thoughtful and informed approach, you can determine whether anHVAC zoning systemis the right solution for your home’s specific needs.





